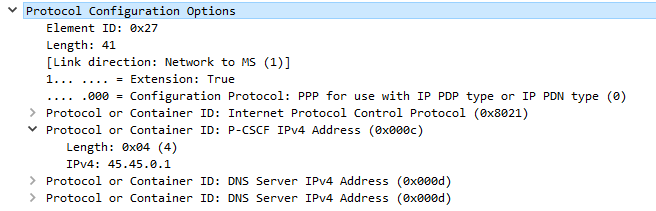
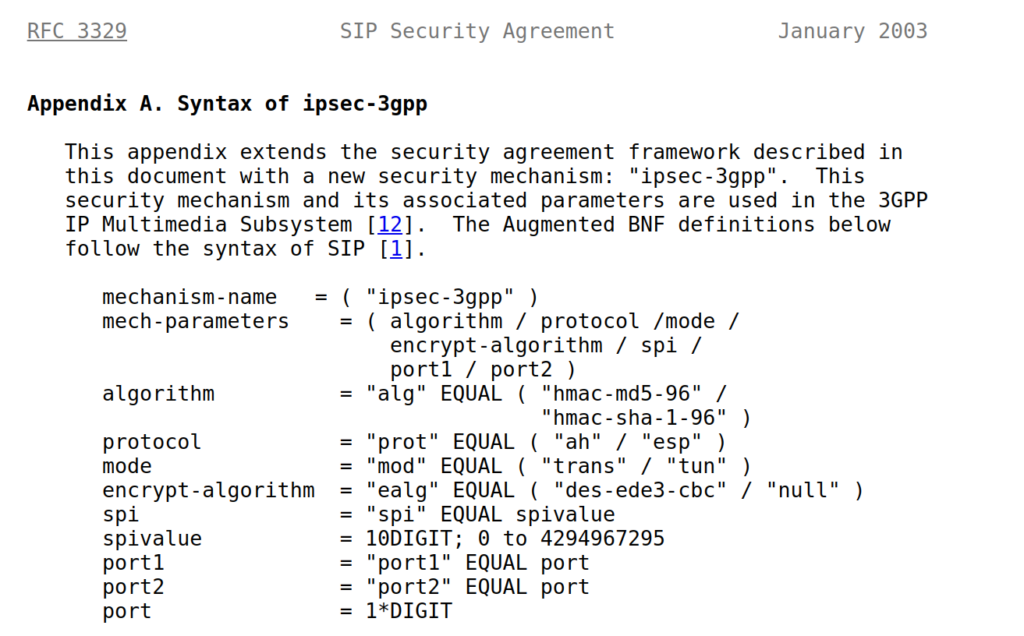
The Australian telecommunications industry was deregulated in 1997, meaning customers could have telecommunications services through a Carriage Service Provider (CSP) of their choice.
In order to increase competition and make it easier to move to a different CSP, the ACMA (Or as they were then the ACA) declared that Local Numbers (Geo numbers / land lines) were a “Portable Service”. This meant that if a customer didn’t like their current Carriage Service Provider (CSP) they could give them the flick (making them the Loosing Carrier), move to a new CSP (Gaining Carrier) but keep their existing phone numbers by moving them to the new carrier in a process known as Local Number Portability (LNP).
The Local Number Portability (LNP) standard was first defined by Comms Alliance in 1999 in ACIF C540 and defines the process of moving numbers between Carriage Service Providers (CSPs), however 22 years later the process can still be a baffling system for many customers, end users and carrier staff to navigate.
Acronyms galore exist and often the porting teams involved themselves aren’t 100% sure what goes on in the porting process.
In 1997 ISDN was first still an emerging technology and porting was typically a customer moving from one PSTN / POTS line provided by one CSP to another PSTN / POTS line provided by a different CSP – a simple port.
Two processes were defined, one for managing simple ports involving moving one simple number from one CSP to another CSP – Called Simple Porting or “Cat A” – which made up the majority of porting requests at the time, and another process for everything else managed by a project manager from the Loosing and Gaining CSP called Complex Porting or “Cat C“.
Since 1997, the advent of the NBN, VoIP, SIP and the announcement that one of Australia’s largest carriers is shutting down their ISDN network by 2020, means that today the majority of ports a business customer will face will be Cat C – Complex Ports.
LNP is an issue worldwide, and ENUM was released to try and make this a bit better, however it had one short trial in Australia a long time ago and hasn’t been looked at since.
Cat A / Simple Number Porting
Simple porting, classified as “Cat A” is used for porting single simple services (numbers).
The Cat A process can only be used for moving a “simple” standalone number – with no additional features – from one carrier to another.
The typical use case for Cat A port is moving a one copper PSTN / POTS line (Active line with no Fax Duet, Line Hunt, etc) from one carrier to another – as I said before, Cat A ports made up the majority of porting requests when the system was first introduced as the vast majority of services were copper POTS lines.
The process is automated at both ends, essentially the carriers send each other the numbers to be moved (more on that later) and their switches automatically process this and begin routing the number.
These ports are typically completed within a few days to a week and the customer gets a notification when the port is completed.
Cat C / Complex Number Porting
For all number porting that don’t meet the very specific requirements of Cat A aren’t met – and sometimes even if they are met, ports are processed as Cat C ports.
Cat C ports require a project manager at both the Gaining Carrier and the Loosing Carrier to agree on the details for the port and the move the numbers, each using their own internal process.
Lead times on Cat C ports are long – and getting longer, so from submitting a port to it’s completion can take 90+ days, and there is no confirmation required to the customer to let them know the services have been ported successfully.
Administrative Process of Ports (CatA & CatC)
Strap yourself in for a whirlwind of acronyms…
The Code does not constrain two or more individual industry participants agreeing to different arrangements
Section 1.3.6
Because of this it means this is the minimum standard, some CSPs have improved upon this between each other, however there’s a bit of a catch 22 in that CSPs have no incentive to make porting numbers out easier, as they’re typically loosing that customer, so the process is typically not improved upon in any meaningful way that makes the customer experience easier.
Without further ado, here’s what Cat A & Cat C ports look like under the hood…
Note: These all assume the Losing CSP is also the Donor CSP. More on that in the LNP FAQ and Call Routing posts.
Cat A – Simple Porting – Process
Summary
Cat A ports are automated – The process involves CSPs transferring formatted data between each other and the process that goes on for these ports.
The Loosing CSP must use the Cat A process if the service meets the requirements to be ported under a Cat A and the Gaining Carrier has submitted it as a Cat A port. This means a Cat A port can’t be rejected by the loosing carrier as not a valid Cat A port to be resubmitted as a Cat C port, if it does actually meet the requirements for Cat A porting. That said numbers that are valid in terms of Cat A can be submitted as a Cat C, this is often cheaper than submitting multiple Cat A porting requests when you have more than 5 or so services to be ported.
Here’s a brief summary of the process:
- Customer requests port and details are validated
- Simple Notification Advice (SNA) is sent to the Loosing CSP via a Porting Notification Order (PNO) – Essentially a form send to the loosing CSP of the intention to port the service
- Loosing CSP sends back SNA Confirmation Advice to confirm the service can be ported
- Electronic Cutover Advice (ECA) sent by gaining CSP to indicate gaining CSP wanting to initiate port
- Loosing CSP provides Donor Routing by essentially redirecting calls to the Gaining CSP
- ECA Confirmation Advice sent by loosing CSP to denote the service has been removed from the loosing CSP’s network & number is with gaining CSP as far as they are concerned
- Losing CSP updates a big text file (PLNR) with a list of numbers allocated to it, to show the numbers have been ported to a different carrier and indicates which carrier
We’ll talk about the technical process of how the data is transferred, what PLNR is and how routing is managed, later on.
In depth process:
Step 1 – Customer Authority
The Gaining CSP must obtain Customer’s Authority (CA) to port number (Section 4.1.2) – Typically this takes the form of a number porting form filled in by the customer, containing a list of numbers to port, account numbers with loosing carrier and date.
If requested by the customer the Loosing CSP must explain any costs / termination payments / contractual obligations to the customer (Section 4.1.4), however the Loosing CSP cannot reject the port based upon an outstanding contract being in place.
Step 2 – Validation
Before anything technical happens, the Gaining CSP must validate the porting request is valid – this means verifying:
- The requested numbers are able to be ported under the selected method (Cat A or Cat C)
- Confirming the date of the Customer Authority is less than 90 days old
- The requested numbers must be recorded
In practice these 3 steps are typically handled by a single form filled out by the customer in the first step. (Section 4.1.5)
If requested by the Loosing CSP this Customer Authority information has to be given to the Loosing CSP. This typically happens in cases of disputed ownership / management of a number.
Step 3 – The SNA PNO
Once the Gaining CSP is satisfied the port is valid, a Simple Notification Advice (SNA) is sent to the Loosing CSP via a Porting Notification Order (PNO) (Section 4.2.2).
The PNO is essentially a form that includes:
- Area Code & Telephone Number of service to be ported
- Service Account number with Loosing CSP
- Porting Category set to Cat A
- Date of Customer Authority
The Loosing CSP must then validate this info, by checking: (Section 4.2.4)
- The requested number is a Simple service (Meets the requirements of Cat A)
- Is with the Loosing CSP (Has not been ported to another carrier already)
- Is not disconnected or pending disconnection at the time the SNA was submitted
- The Customer Authority (CA) date is not more than 90 days old
- Does not currently have a port request pending
After the Loosing CSP has gone through this they will send back a SNA Confirmation Advice if the port request (SNA PNO) is valid or a SNA Reject Advice along with the phone number and reason for rejection if the port request is deemed invalid.
The confirmation, if SNA Confirmation Advice is received, is deemed valid for 30 days, after which the process would have to start again and the SNA PNO would have to be regenerated.
Step 4 – Electronic Cutover Advice (ECA)
After the Loosing CSP sends back a SNA Confirmation Advice, the gaining carrier sends the Loosing Carrier an Electronic Cutover Advice (ECA) via the Final Cutover Notification Interface (Section 4.2.24 ).
When the Loosing CSP get the ECA it’s showtime. The Loosing CSP checks that there’s a valid SNA in place for the number to be ported and that it’s less than 2 days old (Section 4.2.27).
If the Loosing CSP is not satisfied they send back a ECA Reject Advice listing the reason for rejection within 15 minutes (Section 4.2.32).
If all looks good, the Loosing Carrier sends the Gaining CSP back a ECA Confirmation Advice within 15 minutes (Section 4.2.33).
Now is when the magic happens – the Loosing CSP “ports out” that number via their internal process, for this they provide temporary Donor Transit Routing – Essentially redirecting any calls that come into the ported number to the new carrier.
Finally the Loosing CSP sends a Electronic Completion Advice (ECA) to confirm they’ve processed the port out from their network (Section 4.2.34).
Within a day of the port completing, the Losing CSP updates the Ported Local Number Registry (PLNR) to show the service has been ported out and the identifier of the gaining carrier the number has been ported to. PLNR is nothing more than a giant text file containing a list of all the numbers originally allocated to the Loosing CSP and the carrier code they should now be routing to, this data is published so the other CSPs can read it.
Other CSPs read this PLNR data and update their routing tables, meaning the calls will route directly to the new Gaining CSP, and the Donor Routing can be removed on the Losing CSPs switch.
Cat C – Complex Porting – Process
Summary
Cat C ports are a manually project managed, and unlike Cat A are not automated.
This means that the Loosing and Gaining CSP must both allocate a “project manager”, the two to liaise with each other (typically via email) to confirm the numbers can be ported and then find a suitable time to port the numbers, finally at the agreed upon date & time each side kicks off their own process to move the numbers and confirm when it’s done.
Porting Number Validation – PNV
Before a Cat C port can be initiated the PNV process is typically called upon to validate the port won’t get rejected. This isn’t mandatory but is often used as PNV is processed relatively quickly which means any issues with the services can be worked out prior to submitting the port request.
The submitted PNV request is very similar to the actual Cat C porting request (CNA), containing the customer’s details and list of services to be ported.
The loosing CSP returns the list of numbers each with a response code denoting particulars of the service, and if rejected, a rejection code.
Response Codes:
| Reason Code | Reason |
| P | Prime/Directory Service Number |
| A | Associated Service Numbers |
| S | Standalone Number |
| R | Reserved Number |
| D | Exchange based diversion |
| SS | Secondary Service linked to this Number (e.g. DSL) |
Reject Codes:
| Code | Reason | |
| 1 | Invalid Customer Authorization date | Whole Request |
| 2 | Insufficient information supplied | Whole Request |
| 3 | Telephone Number appears to belong to a completely different end customer | Per Number |
| 4 | Telephone Numbers relate to cancelled services or services pending cancellation | Per Number |
| 5 | Missing / invalid PNV Sequence Number | Per Number |
| 6 | Telephone Numbers in the PNV request relate to services which are billed by a service provider other than the Losing Carrier. | Per Number |
| 7 | Telephone Numbers are not found / not present on Losing Carrier’s Network | Per Number |
(Section 4.3.8)
It’s worth noting the main reason PNV is used so heavily in Cat C ports is if a batch of numbers / services are requested to be ported in a single Cat C porting request, if any one of those numbers gets rejected the whole port will need to be resubmitted, hence it being important that before submitting the numbers to be ported, the Gaining CSP verifies they can be ported via the PNV process.
The PNV does not guarantee a physical audit of the services, but rather an audit of available electronic data by the loosing CSP. It’s also only valid for the day of issue, so services can change between a PNV coming back clear and the port request being rejected.
99% of PNV requests should be processed within 5 business days. (Section 4.3.9)
Step 1 – Complex Notification Advice (CNA)
To initiate the port the gaining CSP submits a Complex Notification Advice (CNA) to the loosing CSP.
This contains all the data you’d expect, including customer’s details and the list of services/numbers to be ported, along with a batch number that’s unique to the Gaining CSP (Like a ticket / request number) and Gaining CSP’s Project Manager – The staff member as the Gaining CSP that will be responsible for the port.
Upon receipt, the Loosing CSP sends back a CNA Receipt Advice to confirm they’ve received and begins validating the CNA in a process very similar to the PNV process. (Section 4.4.1)
Step 2 – CNA Confirmation Advice
If verification fails and the CNA request is deemed not valid the CNA is rejected by the Loosing CSP, who sends back a CNA Reject Advice response. This response will contain a list of services and the reject code for each rejected service as per the PNV process.
If the CNA is deemed valid, the Loosing CSP responds with a CNA Confirmation Advice message, containing the Loosing CSP’s project manager for this port, along with the Gaining CSP’s batch number to the Gaining CSP.
This is sent in a batch file along with other CNA Confirmation Advice messages within 5 days. (Section 4.4.6)
Step 3 – Complex Cutover Advice (CCA)
Once the Gaining CSP has the CNA Confirmation Advice the project manager for the port at the Gaining CSP contacts the nominated project manager at the Loosing CSP and the two have to agree on a cutover date and time for the port. (Section 4.4.8)
The agreed date and time of the port is sent by the Gaining CSP to the Loosing CSP in the from of a Complex Cutover Advice (CCA) containing the Gaining CSP batch number and agreed date & time. (Section 4.4.27)
If the details of the CCA are valid from the Loosing CSP’s perspective, the Loosing CSP sends back CCA Confirmation Advice to confirm receipt.
Step 4 – The Porting
At the agreed upon date & time both CSPs are to execute the port from their organization’s perspective.
Typically the loosing CSP provides Donor Transit Routing forwarding / redirecting calls to the ported out number to the new CSP.
There is no completion advice and no verification the port has been completed successfully required by the code. (Section 4.4.48)
Within a day of the port completing, the Losing CSP updates the Ported Local Number Registry (PLNR).
Other CSPs read this PLNR data and update their routing tables, meaning the calls will route directly to the new Gaining CSP, and the Donor Routing can be removed on the Losing CSPs switch.
If you’ve made it this far I’m amazed. I’ve written two more posts on LNP that are relvant to this one, one with an FAQ on number porting, and another with info on how call routing in LNP works.