I’m a bit of a radio nerd & I’ve worked Satellites before, so the Skymuster / LTSS program had me curious. So here’s some nitty-gritty details on NBNCo’s Skymuster Satellite service.
The Payload
NBNco called the LTSS (Long Term Satellite service) but before launch they re-branded as “Skymuster”.
NBNco provided an Interim service called ISS (Interim Satellite Service). before the launch. IPSTAR satellite (Formerly ABG) and Optus services delivered this. Both of these had limited bandwidth and has since been largely replaced by the Skymuster / LTSS.
NBNCo contracted Space Systems / Loral, a US based satellite manufacturer to design and build the payloads. It’s based on the SSL 1300 platform.
When deployed, the payload itself measures 26 metres long, 9 metres tall and 12 metres wide, and weighs in at 6400Kg. Before deployment, in the satellite’s compressed form it fits within a 5-meter launch-vehicle fairing.
Communication to earth is via Ka-band frequencies which allows for greater density of spot beams and frequency reuse. However, capacity improvement through higher frequencies does come with some tradeoffs. Ka-band frequencies, are more susceptible to weather related conditions compared to Ku-band frequencies. Directional accuracy becomes way more important when aligning the customer dishes in Ka band also.

| Direction | Min Freq | Max Freq |
| Earth to Satellite | 27Ghz | 31Ghz |
| Satellite to Earth | 17.7Ghz | 22Ghz |
These emissions are within the range of the higher end software defined radio receivers. I’m curious to see what’s being transmitted, but that’s a topic for another day.
The downlink uses RH and LH circular polarisation.
The Journey
SSL assembled the satelite in California.
SSL staff packed it into a crate and loaded into the belly of an Antinov An-124 which is flown to the launch site.




There are two Skymuster Satellites, NBN-Co 1A & 1B. 1B provides infill / capacity layer for 1A but both are identical. If the 1A satellite was lost during launch / deployment, 1B could be sent up in it’s place. This is still a real risk when launching anything.
NBN-Co 1A was the first launched, riding on a Ariane-5ECA from Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana, South America. 1A launched on 30.09.2015 and 1B launched 05.10.2016 in the same configuration.
After launch to a transit orbit, the satellites had to navigate up into a geostationary orbit at ~36,000Km. This was done using it’s 4 × SPT-100 plasma thrusters, which are exactly as cool as they sound. The final navigation process took up 40% of the fuel in the satellite. Fuel is the determining factor for the expected ~15 year lifetime of the two satellites.

Once in final position SSL performed 2 months worth of tests referred to as “In Orbit Testing”. SSL then handed over operational Telemetry, Tracking and Command (TT&C) to Optus Satellite (Singtel). Optus are tasked with keeping it in it’s current position.
Customer Hardware
Ericsson manage the installation, and subcontract to Hills and Skybridge for the actual work.
Out Door Unit (ODU)
There are currently 3 Satellite Antenna options that are available for
installation, 80cm, 1.2m & 1.8m.

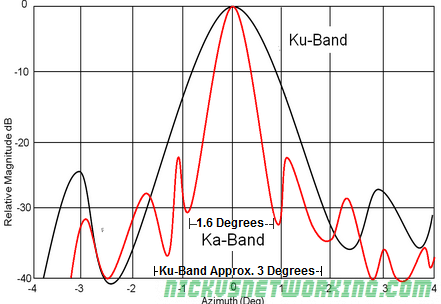
Narrower Ka-Band signals drops off more rapidly than Ku-Band signals. This means that aligning the Ka-Band antenna within the degrees of usable Azimuth within the Line of Sight maximises the antenna gain.
Required accuracy for each of the antennas:
- 80 cm: 1.4 degrees,
- 120 cm: 1.0 degrees
- 180 cm: 0.7 degrees
The below graph shows being off by 1 degree from the required accuracy, leads to -30dB drop. This translates to a power ratio of 1000, or 1/1000 of the power if correctly aligned.
The alignment process is done by the installer pointing the dish in the correct azimuth / elevation. This is based on compass / inclinometer readings, or smart phone apps. Once a rough alignment has been set, a tone-generator on the TIRA is used to align the dish.
This process requires a 16 digit installation key.
The key containing the frequency used in the installation, beam Assignment & TRIA Polarisation (The 6w version has automatic (Polarisation).
That’s entered into the installation setup page at:
TIRA’s has a built in Tone Generator which is used to “Point and Peak” the dish from the roof. The tones are:
- Heartbeat 3KHz
- Pointing Tones 2.5 – 3.1KHz
- Peaking Tones 2.5, 2.95, 3.1 and 3.3KHz
ViaSat have videos on how the alignment process is performed.
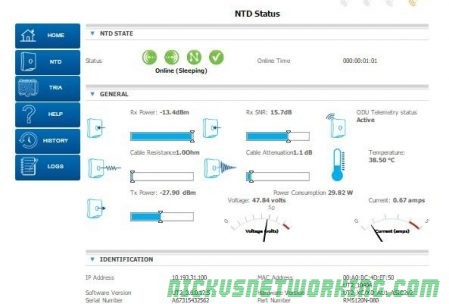
IDU (Modem) / NTD
The modem itself is manufactured by ViaSat. I can’t find any specifics it seems to be in the RM511x line of Satellite modems.
There were some issues with a firmware update on these in 2018, that saw firmware getting rolled back.
The modems / IDU / NTDs for the ISS are not compatible with the LTSS.
There’s some nice teardown photos of a similar ViaSat modem here.



TRIA (Transmit/Receive Integrated Assembly )
The TRIA is the equivalent of a feed horn, an all in one Tx/Rx assembly. They are available in 3w and 6w variants, based on the estimated signal levels of the installation location. That’s determined by factors like high rain areas or if the subscriber is on the edge of a beam.


The 6W version has an extra F-Connector for the required DC power injection. The 6w version also has a two F-Connector gang-plate / wallplate when installed for the second RG6 run to power it.

Interestingly there’s a minimum length of cable run (8m) specified for these installations. Anything less than 8m leads to lower resistance and possible overheating.
There is a minimum length of 8m for the cable run this is very
important as it provides the right amount of cable resistance so
the modem does not get hot and over heat. Max cable run is 50m.










Configuration
Transparent Performance Enhancing Proxy (TPEP)
TPEP aka Web Acceleration, is a service offered by NBNco to spoof TCP replies, to make the handshake more efficient. It can, unsurprisingly, lead to headaches accessing services, particularly those that employ TLS.
Web Interface
http://192.168.5.100:8080/xWebGateway.cgi
user name = ADMIN and the password = operator (lower case)
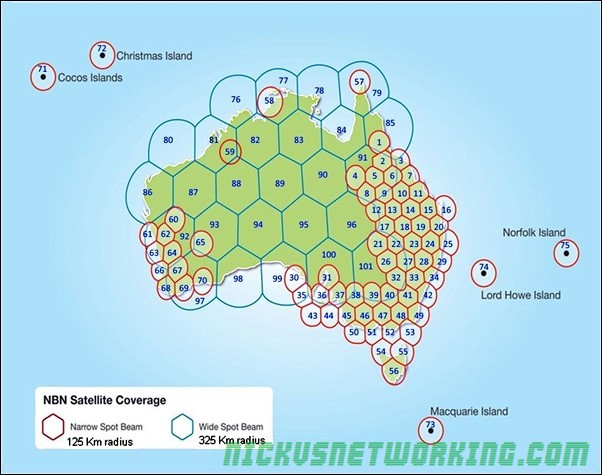
Beam Selection
The installer key sets the beam, and his can be remotely changed by NBNco MAC / NOC team.
BIRRAUS have a good article explaining the spot beams available.
Educational Port
Like the other NBNco NTDs, there are multiple UNI-D ports available on the Skymuster modem allowing segregation of services.
One option that seems to be gaining traction is a dedicated port on the modem for educational use, on one of the UNI-D ports on the modem.
Educational Ports are configured to allow access for remote / distance education students.
The local state government sets pricing, speeds and data usages.
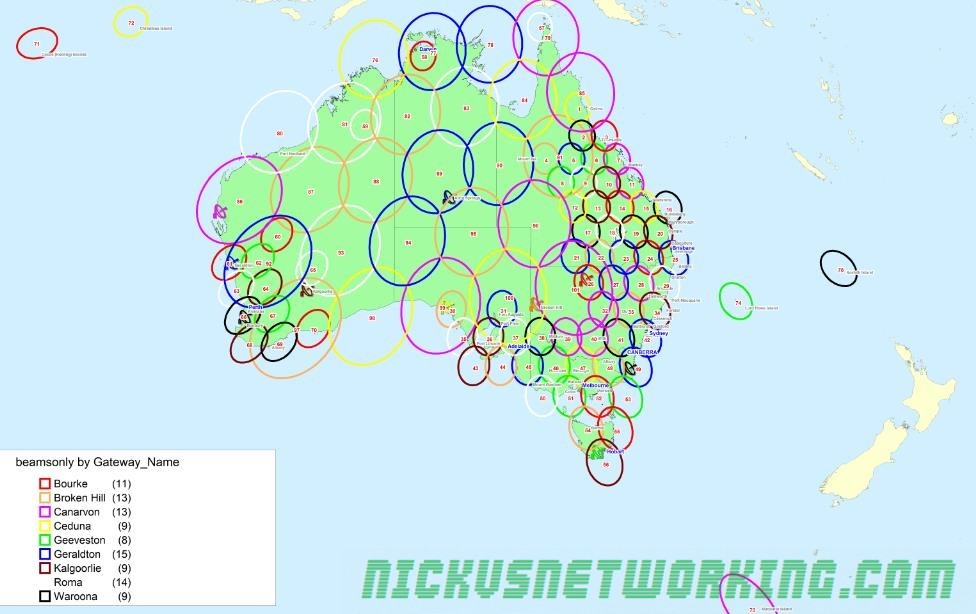
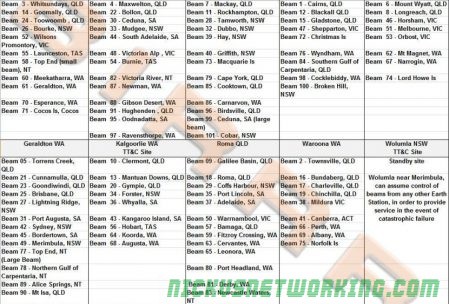
Ground Stations
There are 9 active and one standby ground stations, geographically spread across Australia, with a standby in Wolumna, NSW. The standby is capable of assuming control for any of the other ground stations.
ViaSat built the equipment and services different spot beams.
Again, BIRRAUS have this covered in their article, but here’s an extract they’ve made listing the ground stations and beams serviced.

Future
Solar Transit
Solar transits happen twice yearly when the satellite is aligned directly between the sun and Australia.
The immense solar radiation from the sun overloads the transceivers on the ground, as they’re positioned at the satelite, with the sun behind it overloading the signals.
This lasts for about 6 minutes twice yearly, and affects different ground stations and each of the satellites at different times.
Copper Cutoff
Currently the copper decommissioning does not apply to Skymuster services. This means customers with a copper POTS line, can keep it indefinitely.
This has lead to headaches with incumbent providers who had intended to decommission / sell off remote exchanges, but will be required under Universal Service Obligation to keep them active.
3rd Satellite
Due to unexpectedly large uptake of Skymuster services, NBNco had floated the possibility of launching a 3rd Satelite in 2020:
Scenario 3: Third satellite – This scenario assumes that NBN Co constructs and launches a third satellite at the end of CY20. This mitigates the need to build some fixed wireless base stations and FTTN distribution areas. The capacity of this satellite will only be partially required to meet NBN Co’s needs
Scenario 4: Third satellite in partnership – This scenario mirrors Scenario 3, but assumes that NBN Co enters into a partnership with an external party to access only the required capacity on a third satellite rather than building and owning it outright.
Source – NBNco Fixed Wireless & Satellite Review
Portable Services
Apart from spot-beam migration, there are no technical limitations preventing portable Skymuster services from becoming a service offered.
Qantas are using this to power the in-flight WiFi on their domestic fleet of 80 Boeing 737 and Airbus A330s. Though it seems that may no longer be the case.
The NBNco launched a fleet of “Road Muster” 4WDs for promotion of the services. They drive from town to town, spruiking the benefits of Skymuster.
On the roof of the 4WD is a Satellite ODU, which seems to be self / remote positioning.

Online sleuthing reveals it’s a EXPLORER 8120 manufactured by Cobham. It featuring auto-acquire, drive-away antenna system using Dynamic Pointing Correction technology. At $32k USD, it’s rather pricey, and outside the range of most grey-nomads and campers.
If a user wanted to manually position the dish, they could using a service like DishPointer.com or Wolfram Alpha. This would give a rough alignment and then the tone generator “Point and Peak” for the fine adjustment.
Layer 3 Services
Skymuster services are setup as L2 services.
NBNCo has highlighted from day 1, the option of using Layer 3 for deliver to enable deep packet inspection.
This would allow them to prioritise traffic more easily / efficiently.
Corrections
Please let me know in the comments if I’ve got anything here wrong.