Network Slicing, is a new 5G Technology. Or is it?
Pre 3GPP Release 16 the capability to “Slice” a network already existed, in fact the functionality was introduced way back at the advent of GPRS, so what is so new about 5G’s Network Slicing?
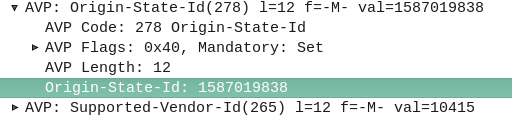
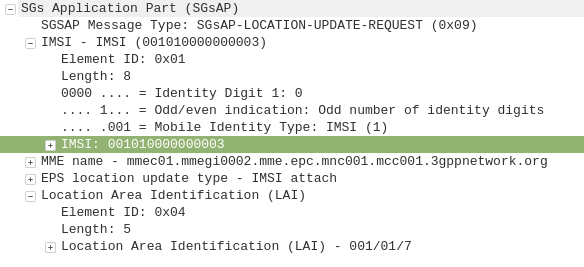
Network Slice: A logical network that provides specific network capabilities and network characteristics
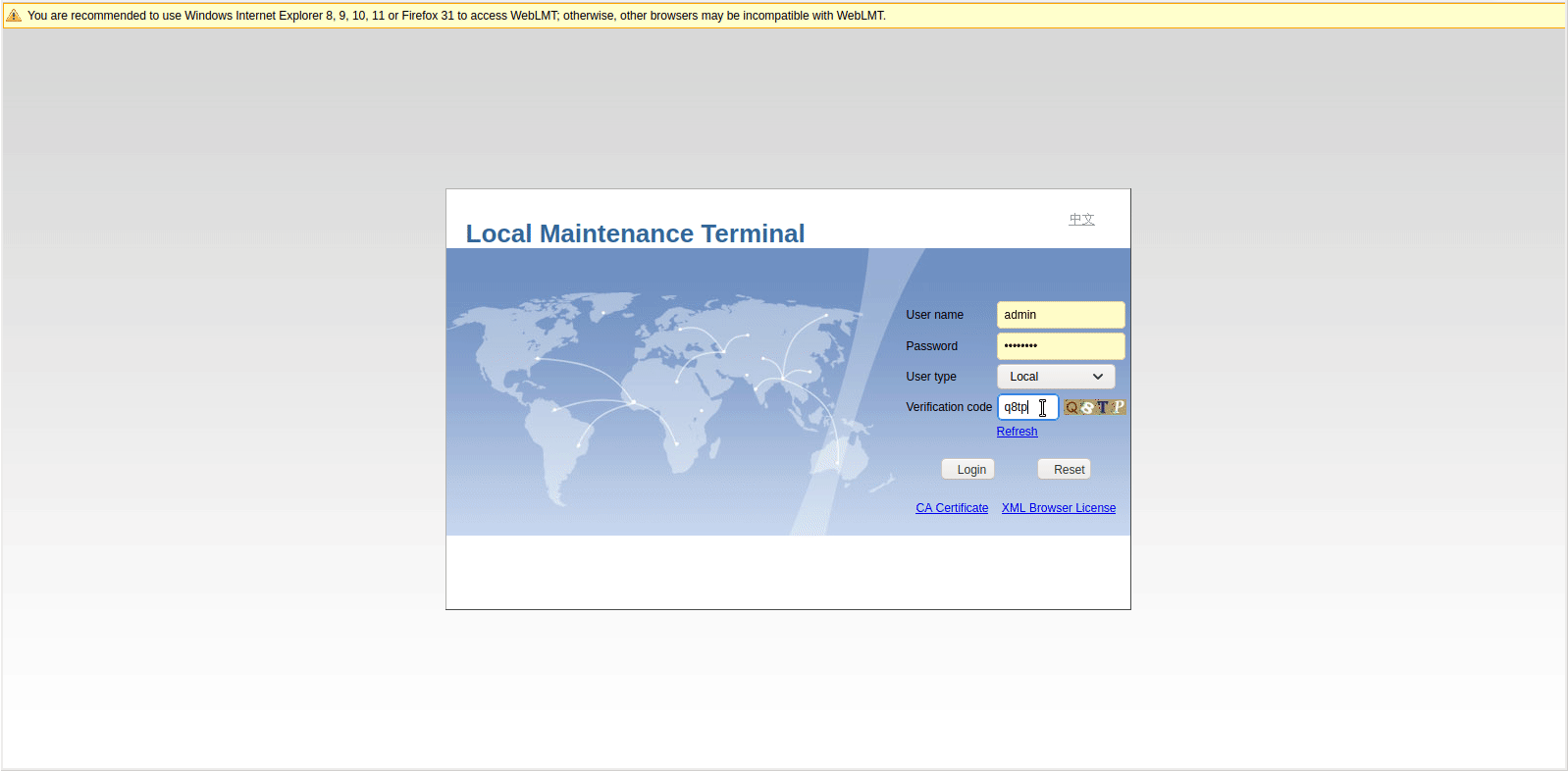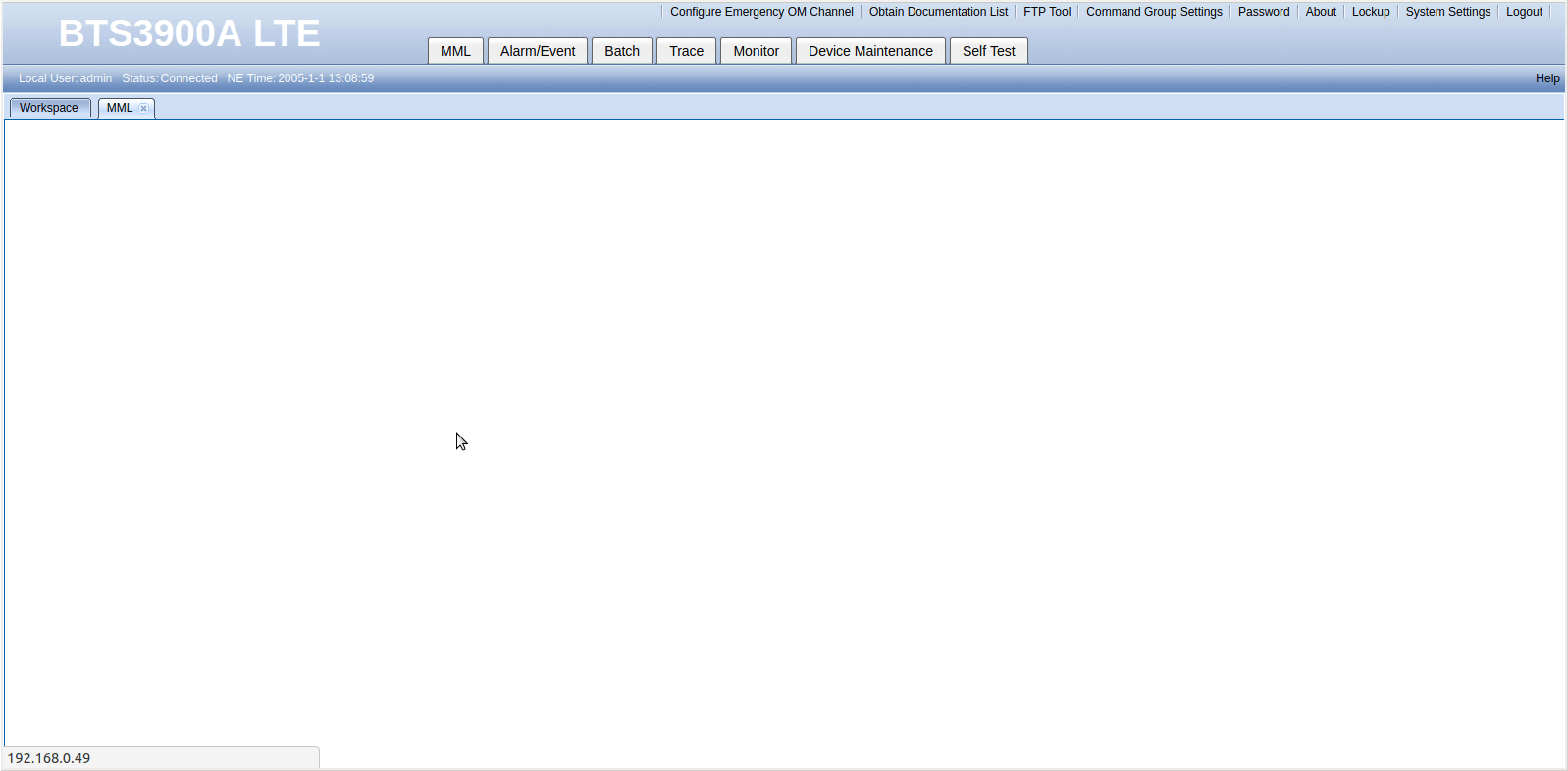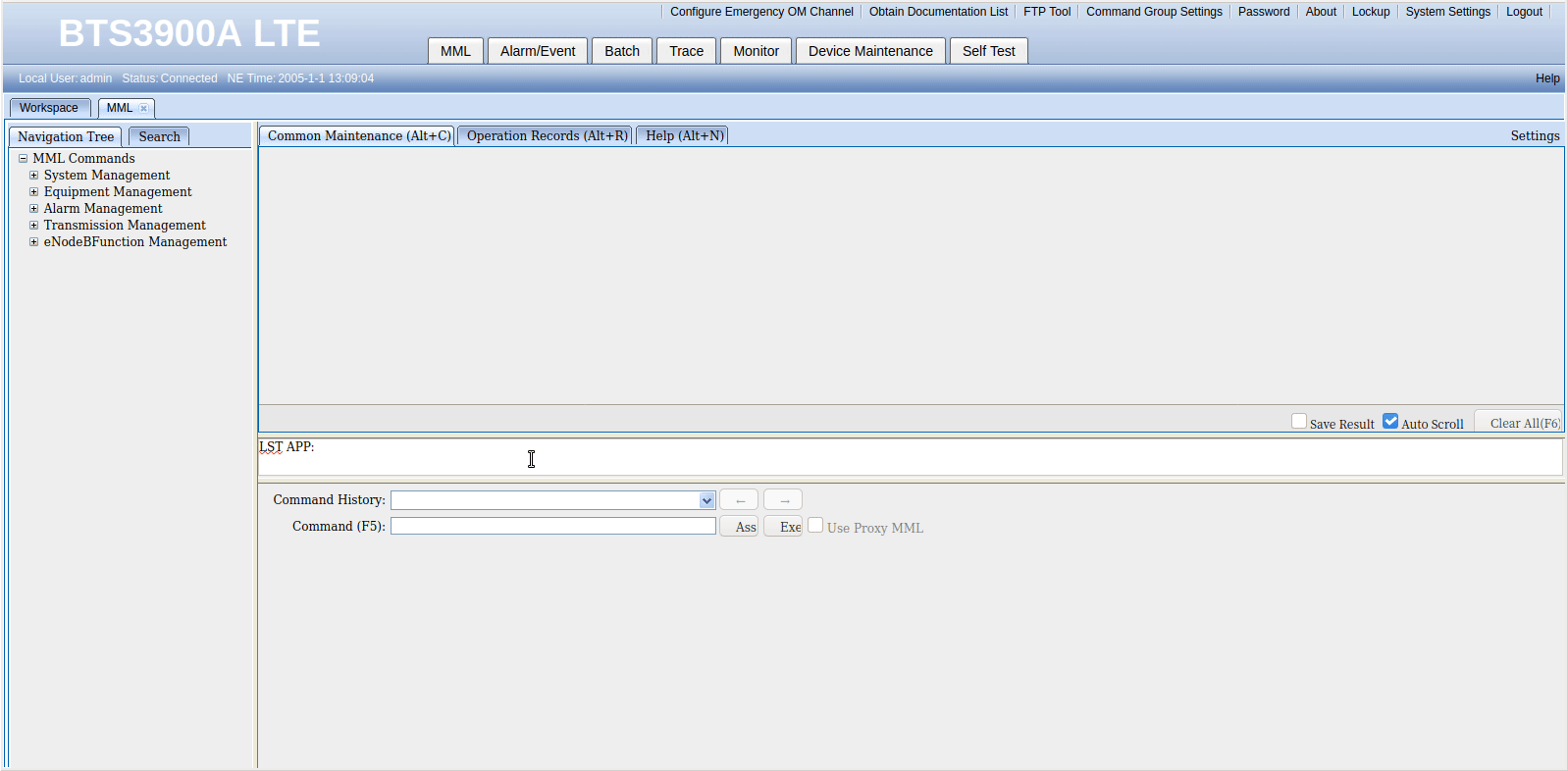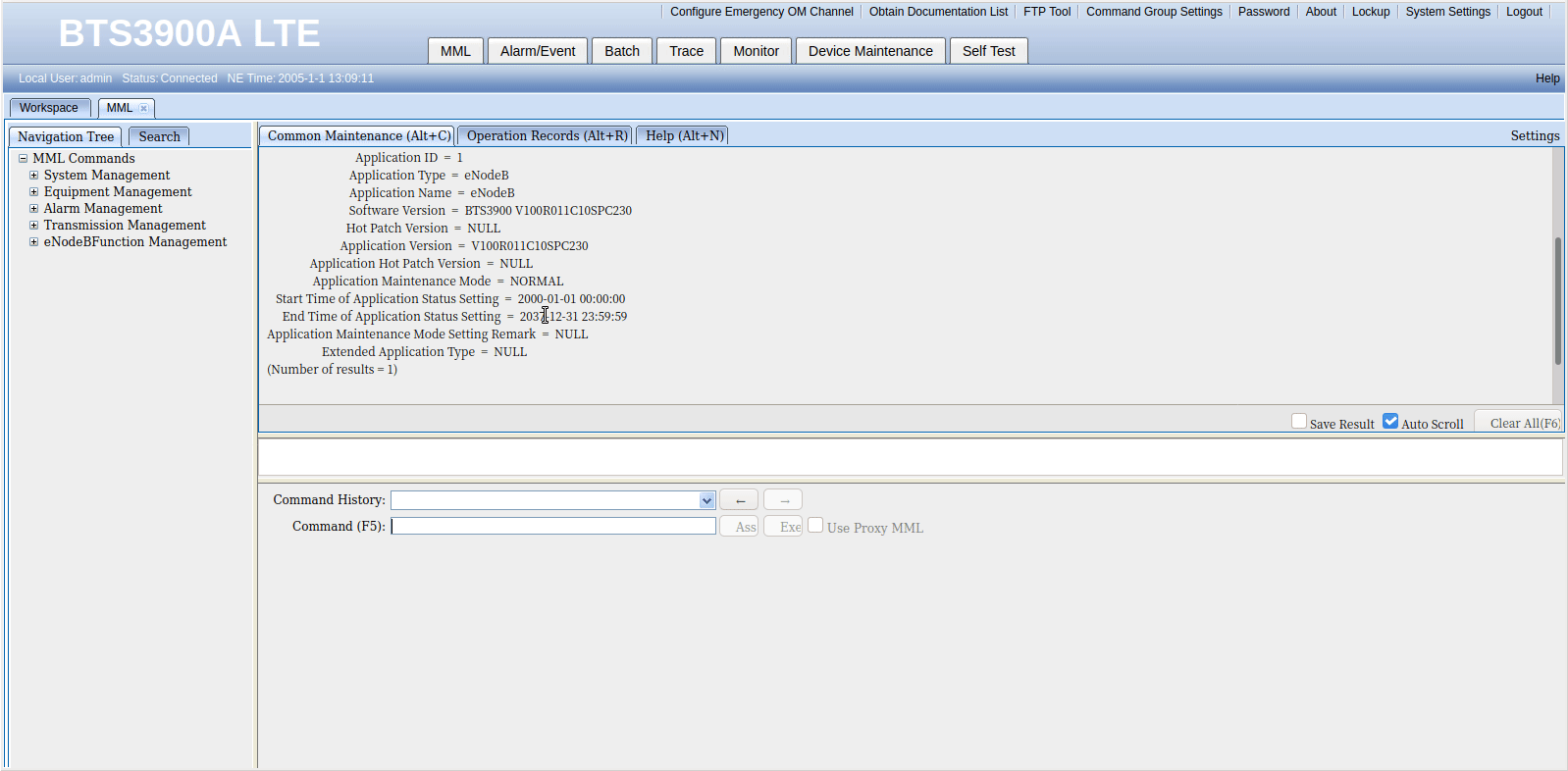
3GPP TS 123 501 / 3 Definitions and Abbreviations
Let’s look at the old and the new ways, of slicing up networks, pre release 16, on LTE, UMTS and GSM.
Old Ways: APN Separation
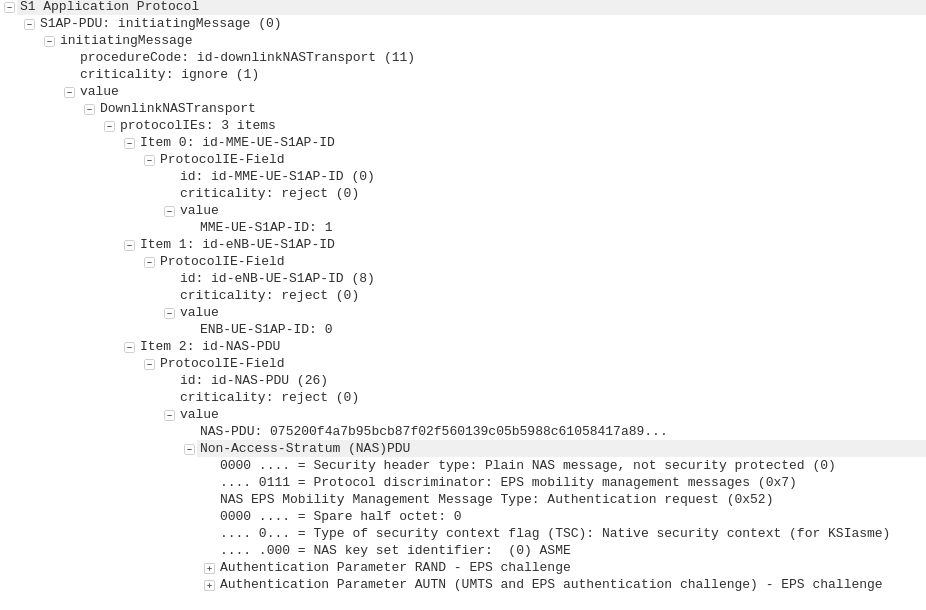
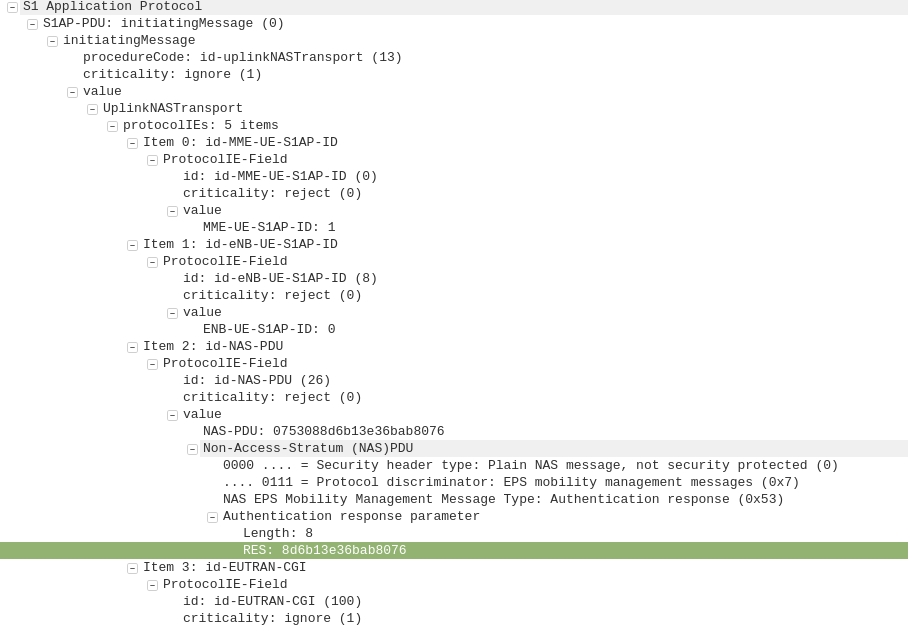
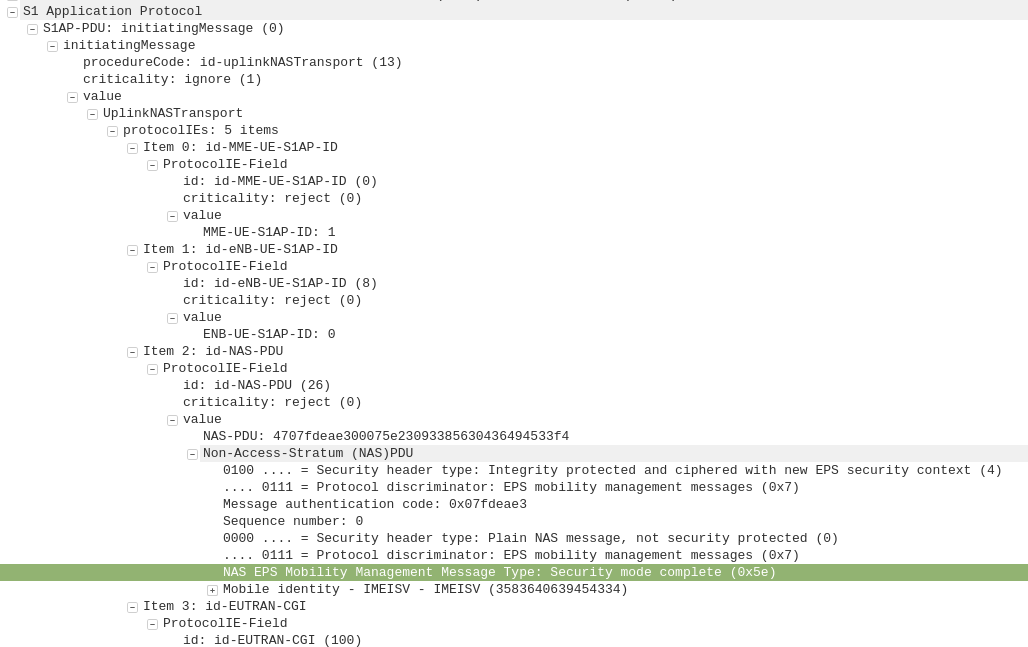
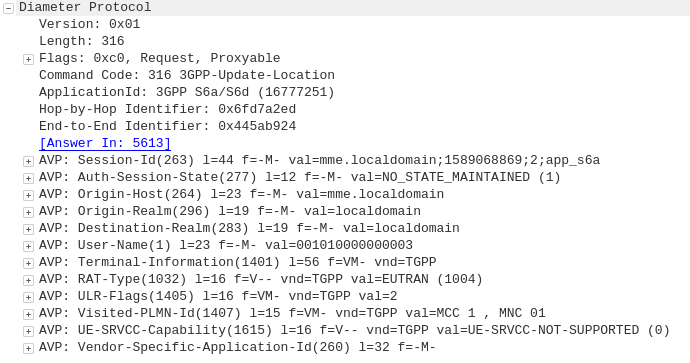
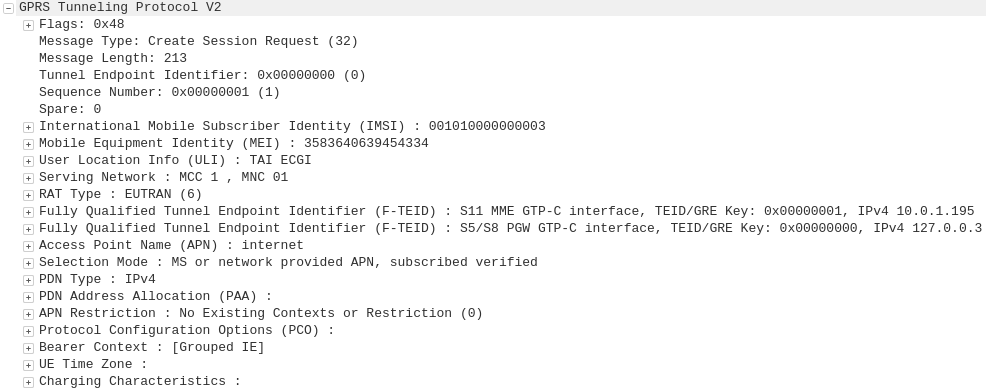
The APN or “Access Point Name” is used so the SGSN / MME knows which gateway to that subscriber’s traffic should be terminated on when setting up the session.
APN separation is used heavily by MVNOs where the MVNO operates their own P-GW / GGSN.
This allows the MNVO can handle their own rating / billing / subscriber management when it comes to data.
A network operator just needs to setup their SGSN / MME to point all requests to setup a bearer on the MVNO’s APN to the MNVO’s gateways, and presoto, it’s no longer their problem.
Later as customers wanted MPLS solutions extended over mobile (Typically LTE), MNOs were able to offer “private APNs”.
An enterprise could be allocated an APN by the MNO that would ensure traffic on that APN would be routed into the enterprise’s MPLS VRF.
The MNO handles the P-GW / GGSN side of things, adding the APN configuration onto it and ensuring the traffic on that APN is routed into the enterprise’s VRF.
Different QCI values can be assigned to each APN, to allow some to have higher priority than others, but by slicing at an APN level you lock all traffic to those QoS characteristics (Typically mobile devices only support one primary APN used for routing all traffic), and don’t have the flexibility to steer which networks which traffic from a subscriber goes to.
It’s not really practical for everyone to have their own APNs, due in part to the namespace limitations, the architecture of how this is usually done limits this, and the simple fact of everyone having to populate an APN unique to them would be a real headache.
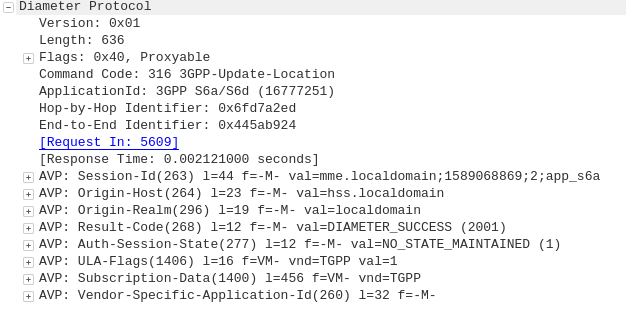
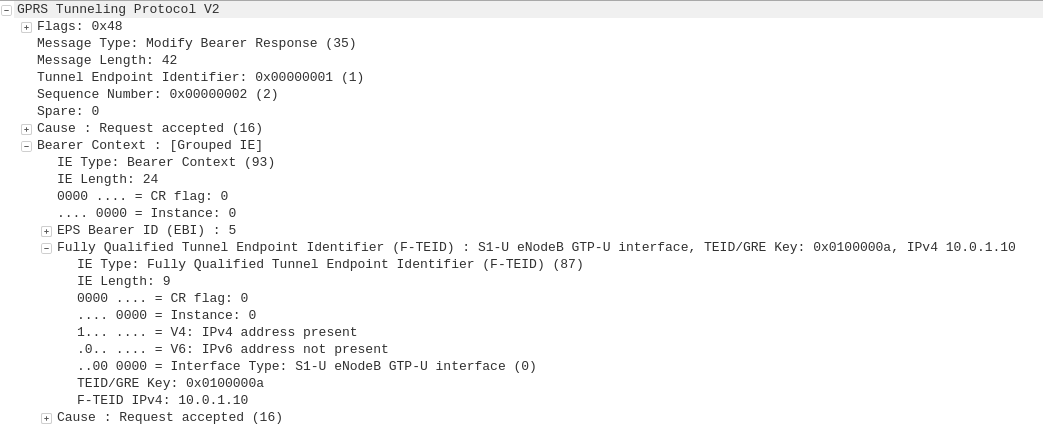
5G replaces APNs with “DNNs” – Data Network Names, but the functionality is otherwise the same.
In Summary:
APN separation slices all traffic from a subscriber using a special APN and provide a bearer with QoS/QCI values set for that APN, but does not allow granular slicing of individual traffic flows, it’s an all-or-nothing approach and all traffic in the APN is treated equally.
The old Ways: Dedicated Bearers
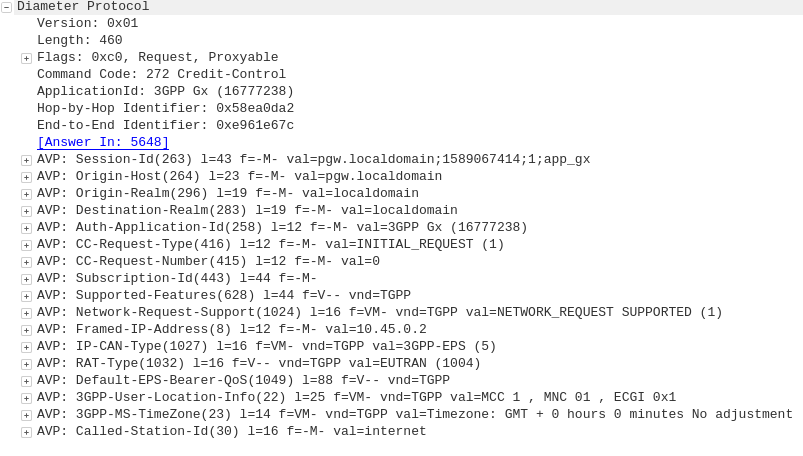
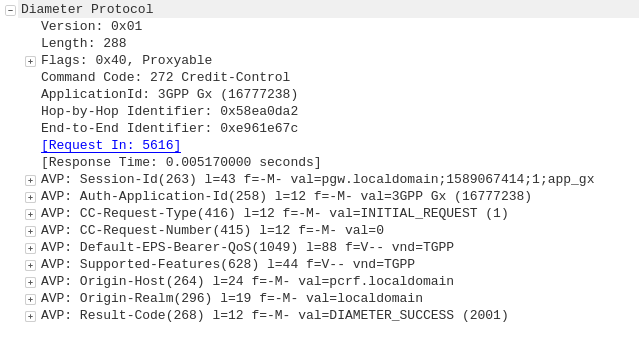
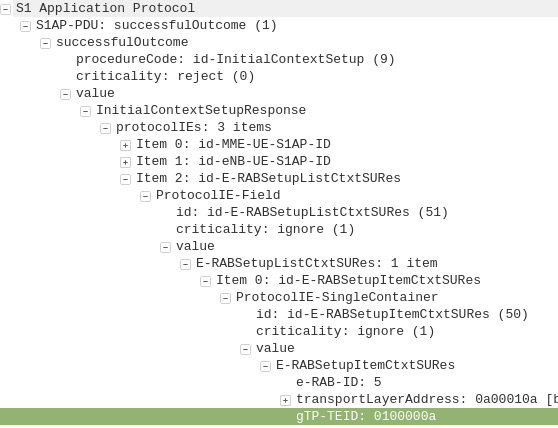
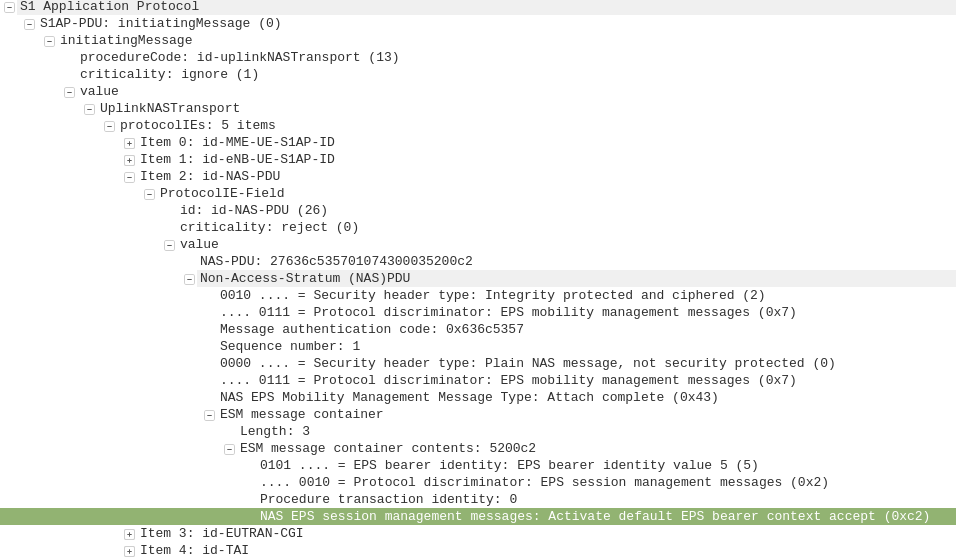
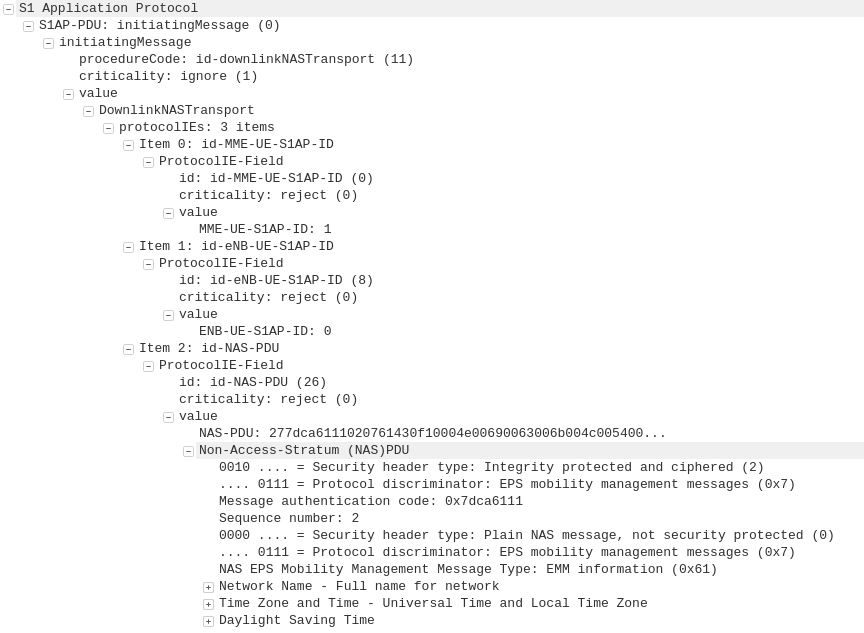
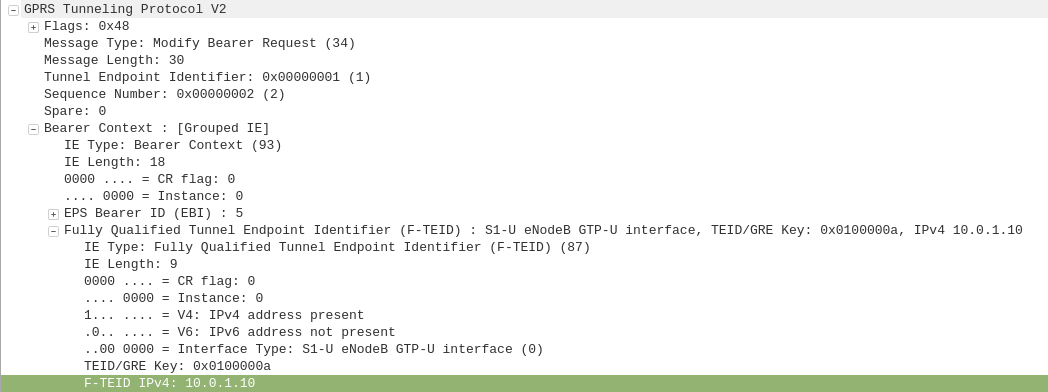
Dedicated bearers allow traffic matching a set rule to be provided a lower QCI value than the default bearer. This allows certain traffic to/from a UE to use GBR or Non-GBR bearers for traffic matching the rule.
The rule itself is known as a “TFT” (Traffic Flow Template) and is made up of a 5 value Tuple consisting of IP Source, IP Destination, Source Port, Destination Port & Protocol Number. Both the UE and core network need to be aware of these TFTs, so the traffic matching the TFT can get the QCI allocated to it.
This can be done a variety of different ways, in LTE this ranges from rules defined in a PCRF or an external interface like those of an IMS network using the Rx interface to request a dedicated bearers matching the specified TFTs via the PCRF.
Unlike with 5G network slicing, dedicated bearers still traverse the same network elements, the same MME, S-GW & P-GW is used for this traffic. This means you can’t “locally break out” certain traffic.
In Summary:
Dedicated bearers allow you to treat certain traffic to/from subscribers with different precedence & priority, but the traffic still takes the same path to it’s ultimate destination.
Old Ways: MOCN
Multi-Operator Core Network (MOCN) allows multiple MNOs to share the same active (tower) infrastructure.
This means one eNodeB can broadcast more than one PLMN and server more than one mobile network.
This slicing is very coarse – it allows two operators to share the same eNodeBs, but going beyond a handful of PLMNs on one eNB isn’t practical, and the PLMN space is quite limited (1000 PLMNs per country code max).
In Summary:
MOCN allows slicing of the RAN on a very coarse level, to slice traffic from different operators/PLMNs sharing the same RAN.Its use is focused on sharing RAN rather than slicing traffic for users.