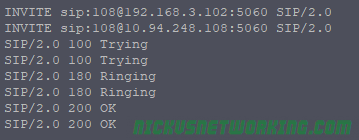
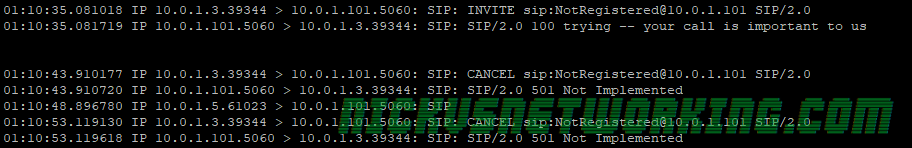
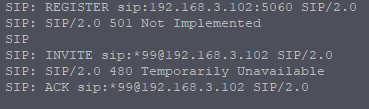
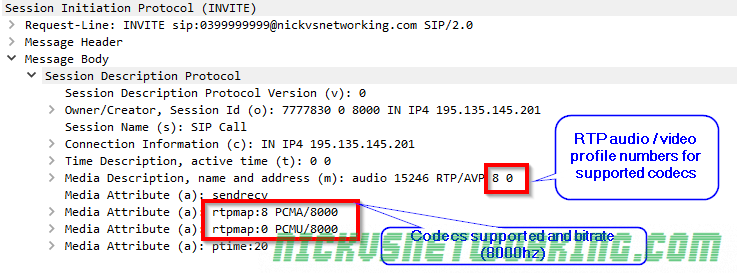
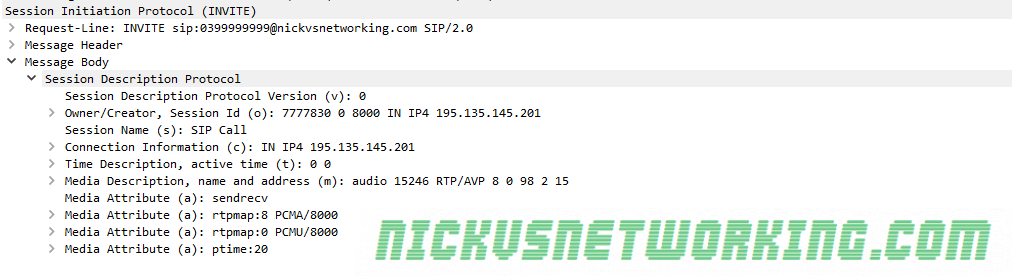
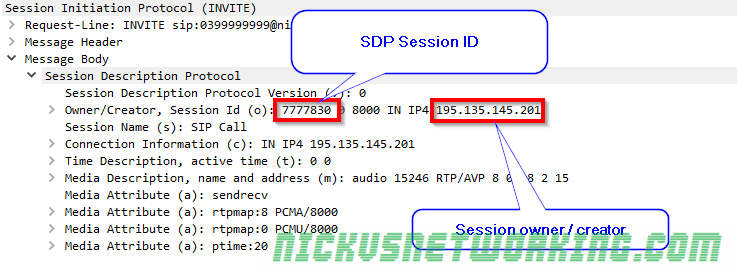
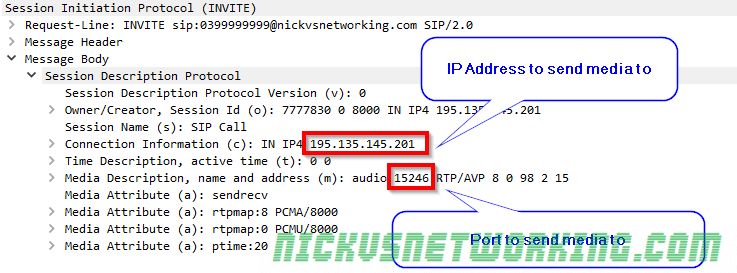
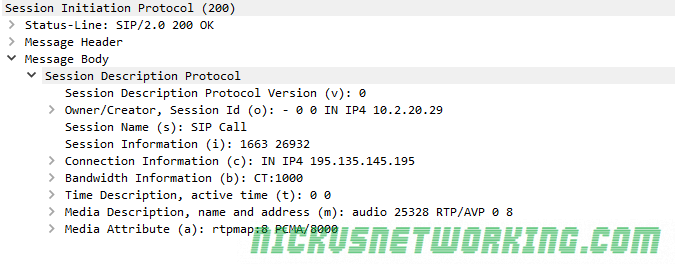
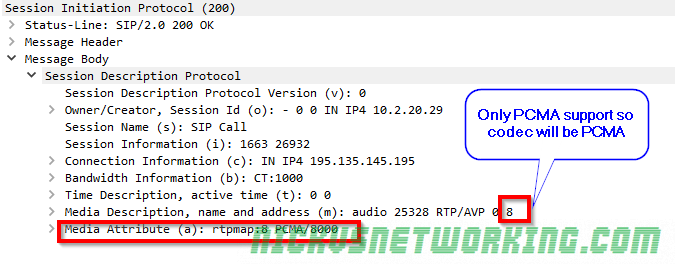
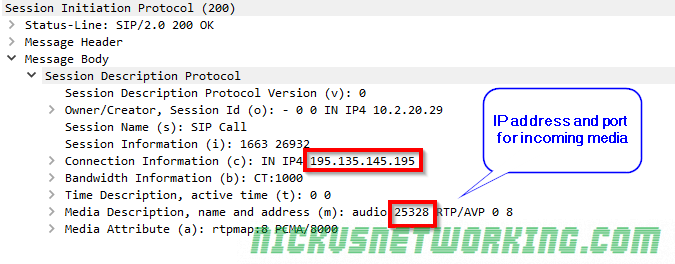
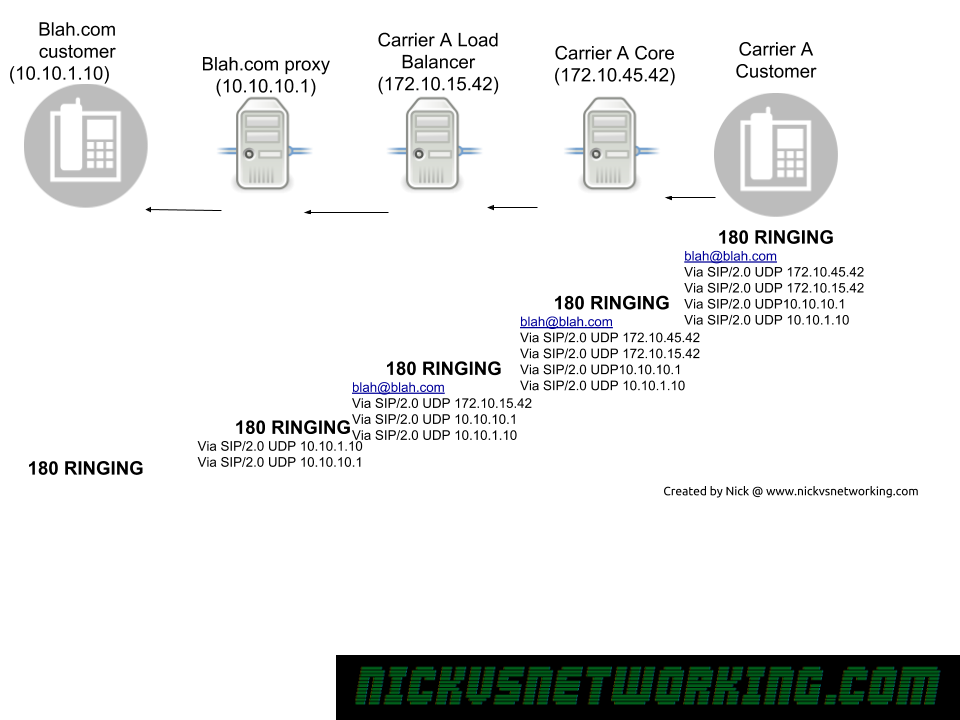
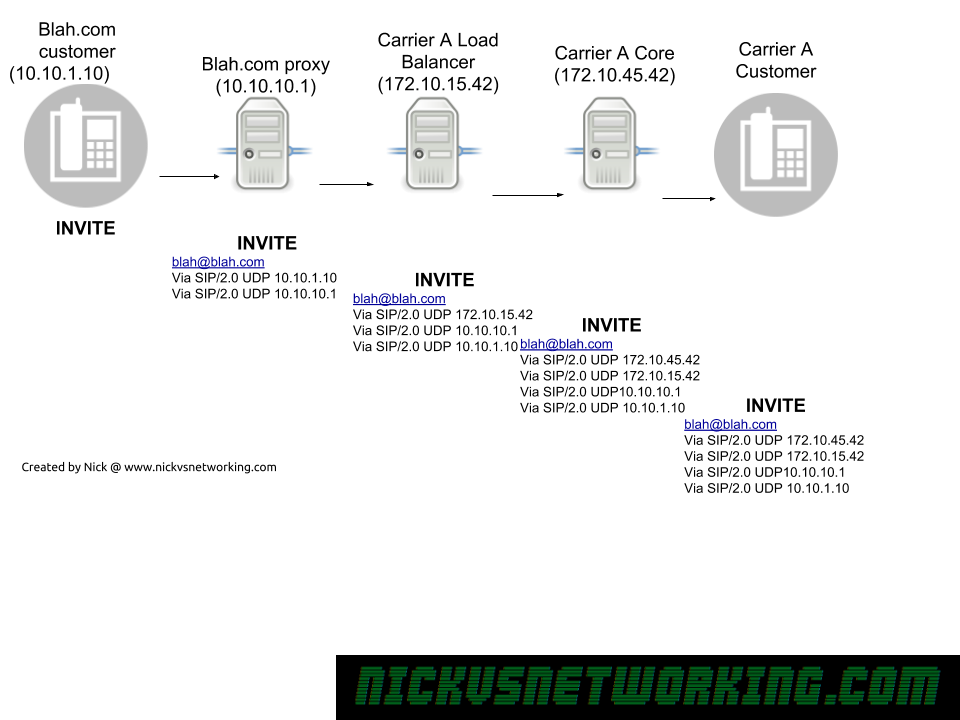
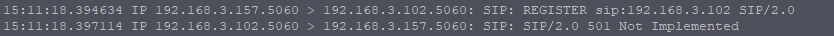In the last tutorial we saw some issues, calls hung up before they were answered (CANCEL), we also would have run into issues with timeouts, issues if the remote end was registered but no longer responding, behind a NAT etc.
We saw a real example of what I touched on on the opener to this series, that you have to deal with everything, and it’s a daunting task.
Kamailio allows you to deal with all these problems yourself, writing your own routing blocks, but it also comes with a bunch of useful routing blocks in the example config, that we can re-use so we don’t need to specify how to manage every little thing ourselves – unless we want to.
So lets add some of these useful routing blocks,
We’ll add this at the start of our request_route{ block
request_route {
if (is_method("CANCEL")) {
if (t_check_trans()) {
route(RELAY);
}
exit;
}
if (!is_method("ACK")) {
if(t_precheck_trans()) {
t_check_trans();
exit;
}
t_check_trans();
}
# handle requests within SIP dialogs
route(WITHINDLG);
So now our config looks like this:
request_route {
if (is_method("CANCEL")) {
if (t_check_trans()) {
route(RELAY);
}
exit;
}
if (!is_method("ACK")) {
if(t_precheck_trans()) {
t_check_trans();
exit;
}
t_check_trans();
}
# handle requests within SIP dialogs
route(WITHINDLG);
if(method=="INVITE"){
if(!lookup("location")){
sl_reply("404", "User not Registered");
exit;
}
lookup("location");
t_relay();
exit();
}
if(method=="REGISTER"){
save("location");
exit;
}
xlog("No idea how to respond to method $rm");
sl_reply("501", "Not Implemented");
}
As you can see we’ve added an if statement to match if the method is CANCEL or ACK, and referenced some routing blocks:
- route(RELAY)
- route(WITHINDLG);
We’ve also added some code to manage ACKs, but we’ll go through that on our lesson on Statefulness, for now just roll with it.
You’ll probably notice if you try and use this config that it won’t work, that’s because we’re referencing these two routing blocks without actually having defined them.
To keep us moving I’ve added all the routing blocks that come with the default Kamailio config, and added in our code to the link below;
GitHub – NickvsNetworking – Kamailio101
And finally we’ll restart and be good to go:

To recap, we added the boilerplate routes that come with Kamailio and referenced them in our code to better handle in dialog responses.
This is because handling all these possible scenarios, like NAT, cancel, no response, REINVITE, UPDATE, etc, etc, would take us ages to cover, and require a pretty good understanding of Kamailio and of SIP in practice.
So use the example I’ve linked above and tune in next time, where we’ll talk about adding security and authentication to our system before we connect it to the outside world.
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 7 – Security in Theory| This Post – Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 6| Previous Post – Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 5 – First Call
Other posts in the Kamailio 101 Series:
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 1 – Introduction
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 2 – Installation & First Run
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 3 – Routing Blocks & Structure
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 4 – Taking Registrations
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 5 – First Call
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 6 – Reusing Code
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 7 – Security in Theory
Kamailio 101 – Tutorial 8 – Security in Practice