The Wiki on the Sangoma documentation page is really out of date and can’t be easily edited by the public, so here’s the skinny on how to setup a Sangoma transcoding card on a modern Debian system:
apt-get install libxml2* wget make gcc wget https://ftp.sangoma.com/linux/transcoding/sng-tc-linux-1.3.11.x86_64.tgz tar xzf sng-tc-linux-1.3.11.x86_64.tgz cd sng-tc-linux-1.3.11.x86_64/ make make install cp lib/* /usr/local/lib/ ldconfig
At this point you should be able to check for the presence of the card with:
sngtc_tool -dev ens33 -list_modules
Where ens33 is the name of the NIC that the server that shares a broadcast domain with the transcoder.
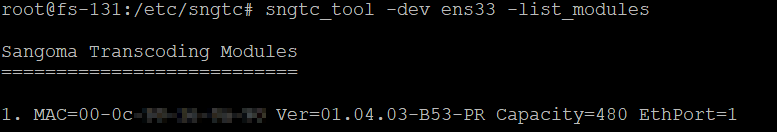
If instead you see something like this:
root@fs-131:/etc/sngtc# sngtc_tool -dev ens33 -list_modules Failed to detect and initialize modules with size 1
That means the server can’t find the transcoding device. If you’re using a D150 (The Ethernet enabled versions) then you’ve got to make sure that the NIC you specified is on the same VLAN / broadcast domain as the server, for testing you can try directly connecting it to the NIC.
I also found I had to restart the device a few times to get it to a “happy” state.
It’s worth pointing out that there are no LEDs lit when the system is powered on, only when you connect a NIC.
Next we’ll need to setup the sngtc_server so these resources can be accessed via FreeSWITCH or Asterisk.
Config is pretty simple if you’re using an all-in-one deployment, all you’ll need to change is the NIC in a file you create in /etc/sngtc/sngtc_server.conf.xml:
<configuration name="sngtc_server.conf" description="Sangoma Transcoding Manager Configuration">
<settings>
<!--
By default the SOAP server uses a private local IP and port that will work for out of the box installations
where the SOAP client (Asterisk/FreeSWITCH) and server (sngtc_server) run in the same box.
However, if you want to distribute multiple clients across the network, you need to edit this values to
listen on an IP and port that is reachable for those clients.
<param name="bindaddr" value="0.0.0.0" />
<param name="bindport" value="9000" />
-->
</settings>
<vocallos>
<!-- The name of the vocallo is the ethernet device name as displayed by ifconfig -->
<vocallo name="ens33">
<!-- Starting UDP port for the vocallo -->
<param name="base_udp" value="5000"/>
<!-- Starting IP address octet to use for the vocallo modules -->
<param name="base_ip_octet" value="182"/>
</vocallo>
</vocallos>
</configuration>
With that set we can actually try starting the server,
Again, all going well you should see something like this in the log:
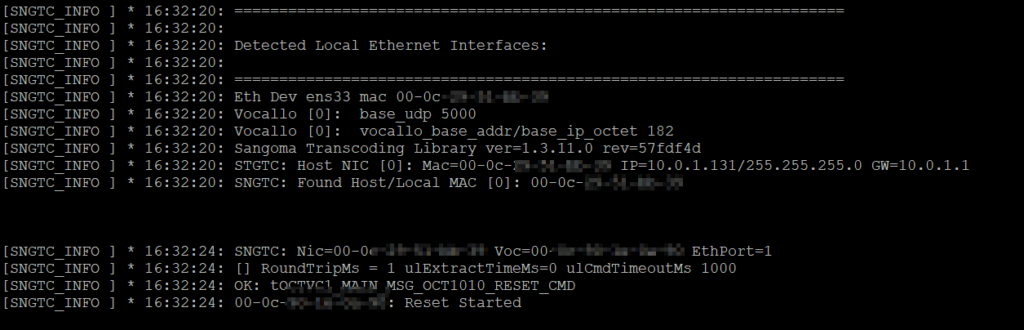
And then at the end you should see:
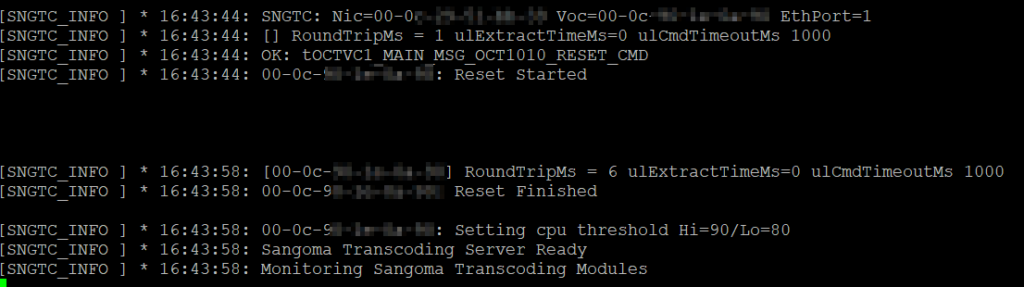
[SNGTC_INFO ] * 16:43:58: [00-0c-xx-yy-zz] RoundTripMs = 6 ulExtractTimeMs=0 ulCmdTimeoutMs 1000 [SNGTC_INFO ] * 16:43:58: 00-0c-xx-yy-zz: Reset Finished [SNGTC_INFO ] * 16:43:58: 00-0c-xx-yy-zz: Setting cpu threshold Hi=90/Lo=80 [SNGTC_INFO ] * 16:43:58: Sangoma Transcoding Server Ready [SNGTC_INFO ] * 16:43:58: Monitoring Sangoma Transcoding Modules
Once we know it’s starting up manually we can try and start the daemon.
sngtc_server_ctrl start
Should result in:
sngtc_server: Starting sngtc_server in safe mode ... sngtc_server: Starting processes... Starting sngtc_server...OK
And with that, we’re off and running and ready to configure this for use in FreeSWITCH or Asterisk.
