These posts focus on the use of Diameter and SIP in an IMS / VoLTE context, however these practices can be equally applied to other networks.
The Location-Information-Request/Answer commands are used so a SIP Server query a Diameter to find which P-CSCF a Subscriber is being served by
Basics:
The RFC’s definition is actually pretty succinct as to the function of the Server-Assignment Request/Answer:
The Location-Info-Request is sent by a Diameter Multimedia client to a Diameter Multimedia server in order to request name of the server that is currently serving the user.Reference: 29.229-
The Location-Info-Request is sent by a Diameter Multimedia client to a Diameter Multimedia server in order to request name of the server that is currently serving the user.
Reference: TS 29.229
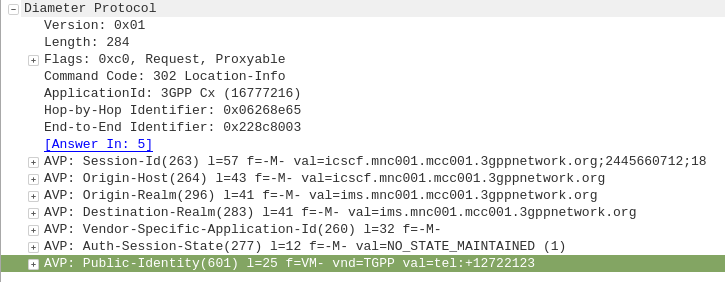
The Location-Info-Request commands is sent by an I-CSCF to the HSS to find out from the Diameter server the FQDN of the S-CSCF serving that user.
The Public-Identity AVP (601) contains the Public Identity of the user being sought.
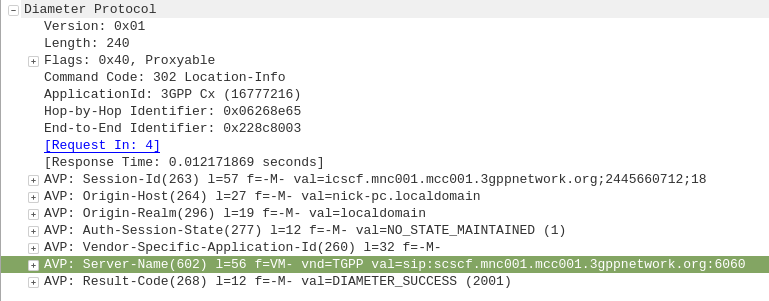
The Diameter server sends back the Location-Info-Response containing the Server-Name AVP (602) with the FQDN of the S-CSCF.
Packet Capture
I’ve included a packet capture of these Diameter Commands from my lab network which you can find below.
Other Diameter Cx (IMS) Calls
User-Authorization-Request / User-Authorization-Answer
Server-Assignment-Request / Server-Assignment-Answer
Location-Info-Request / Location-Info-Answer
Multimedia-Auth-Request / Multimedia-Auth-Answer
Registration-Termination-Request / Registration-Termination-Answer
Push-Profile-Request / Push-Profile-Answer
References:
RFC 4740 – Diameter Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Application