Like in EPS / LTE, there are two ways to send SMS in Standalone 5G Core networks.
SMS over IMS or SMS over NAS – Both can be used on the same network, or just one, depending on operator preferences.
SMS over IMS in 5G
SMS over IMS uses the IMS network to send SMS. SIP MESSAGE methods are used to deliver SMS between users. While most operators have deployed IMS for 4G/LTE subscribers to use VoLTE some time ago, there are some changes required to the IMS architecture to support VoNR (Voice over New Radio) on the carrier side, and support for VoNR in commercial devices is currently in its early stages. Because of this many 5G devices and networks do not yet support SMS over IMS.
I’ve read in some places that RCS – The GSMA’s Rich Communications Service will replace SMS in 5GC. If this is the case, it reflected in any of the 3GPP standards.
SMS over NAS
To make a voice call on a device or network that does not support VoNR, EPS (VoLTE) fallback is used.
This means when making or receiving a call, the UE drops from the 5G RAN to using a 4G (LTE) basd RAN, and then uses VoLTE to make the call the same as it would when connected to 4G (LTE) networks, because it is connected to a 4G network.
This works technically, but is not the prefered option as it adds extra signaling and complexity to the network, and delays in the call setup, and it’s expected operators will eventually move to VoNR,but works as a stop-gap measure.
But mobile networks see a lot of SMS traffic. If every time an SMS was sent the UE had to rely on EPS fallback to access IMS, this would see users ping-ponging between 4G and 5G every time they sent or received an SMS.
This isn’t a new problem, in fact SMS-over-NAS was initially added to 4G (LTE) to allow devices to stay connected to the EPC (4G Core network) but still send and receive SMS, even if the network or device relied on “Circuit-Switched fallback” (A mechanism to drop from 4G to 2G / 3G for voice calls).
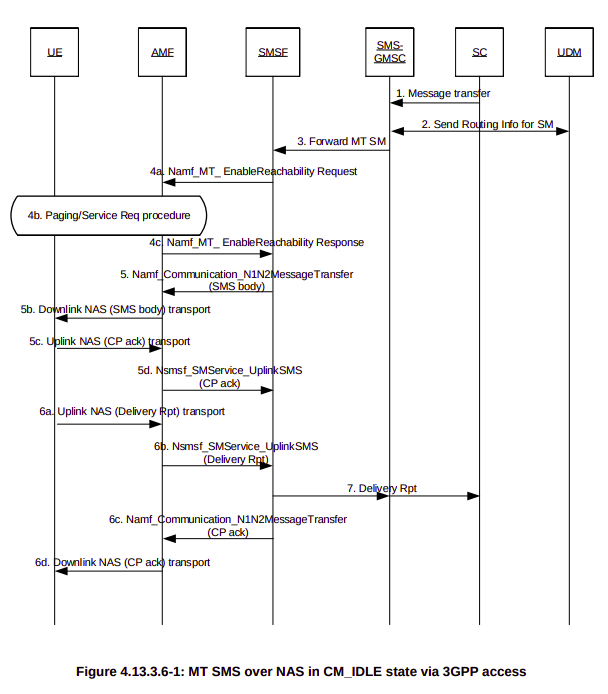
5GC reintroduces the SMS-over-NAS feature, allowing the SMS messages to be carried over NAS messaging on the N1 interface. Voice calls may still require fallback to EPS (4G) to make calls over VoLTE, but SMS can be carried over NAS messaging, minimizing the amount of Inter-RAT handovers required.
The Nsmsf_SMService
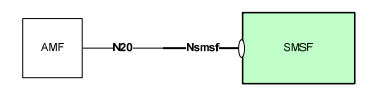
For this a new Service Based Interface is introduced between the AMF and the SMSF (SMS Function, typically built into an SMSc), via the N20 / Nsmsf SBI to offer the Nsmsf_SMService service.
There are 3 operations supported for the Nsmsf_SMService:
- Active – Initiated by the AMF – Used to active the SMS service for a given subscriber,
- Deactivate – Initiated by the AMF – Used to deactivate the SMS over NAS service for a given subscriber.
- UplinkSMS – Initiated by the AMF to transfer the SMS payload towards the SMSF.
The UplinkSMS is a HTTP post from the AMF with the SUPI in the Request URI and the request body containing a JSON encoded SmsRecordData.

Astute readers may notice that’s all well and good, but that only covers Mobile Originated (MO) SMS, what about Mobile Terminated (MT) SMS?
Well that’s actually handled by a totally different SBI, the Namf_Communication action “N1N2MessageTransfer” is resused for sending MT SMS, as that interface already exists for use by SMF, LMF and PCF, and 5GC attempts to reuse interfaces as much as possible.