PyHSS is our open source Home Subscriber Server, it’s written in Python, has a variety of different backends, and is highly perforate (We benchmark to 10K transactions per second) and infinitely scaleable.
In this post I’ll cover the basics of setting up PyHSS in your enviroment and getting some Diameter peers connected.
For starters, we’ll need a database (We’ll use MySQL for this demo) and an account on that database for a MySQL user.
So let’s get that rolling (I’m using Ubuntu 24.04):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mysql-server
Next we’ll create the MySQL user for PyHSS to use:
CREATE USER 'pyhss_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'pyhss_password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'pyhss_user'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;We’ll also need Redis as well (PyHSS uses Redis for inter-service communications and for caching), so go ahead an install that for your distro:
sudo apt install redis-server
So that’s our prerequisites sorted, let’s clone the PyHSS repo:
git clone https://github.com/nickvsnetworking/pyhss /etc/pyhss
And install the requirements with pip from the PyHSS repo:
pip3 install -r requirements.txtNext we’ll need to configure PyHSS, for that we update the config file (config.yaml) with the settings we want to use.
We’ll start by setting the bind_ip to a list of IPs you want to listen on, and your transport – We can use either TCP or SCTP.
For Diameter, we will set OriginHost and OriginRealm to match the Diameter hostname you want to use for this peer, and the Realm of your Diameter network.
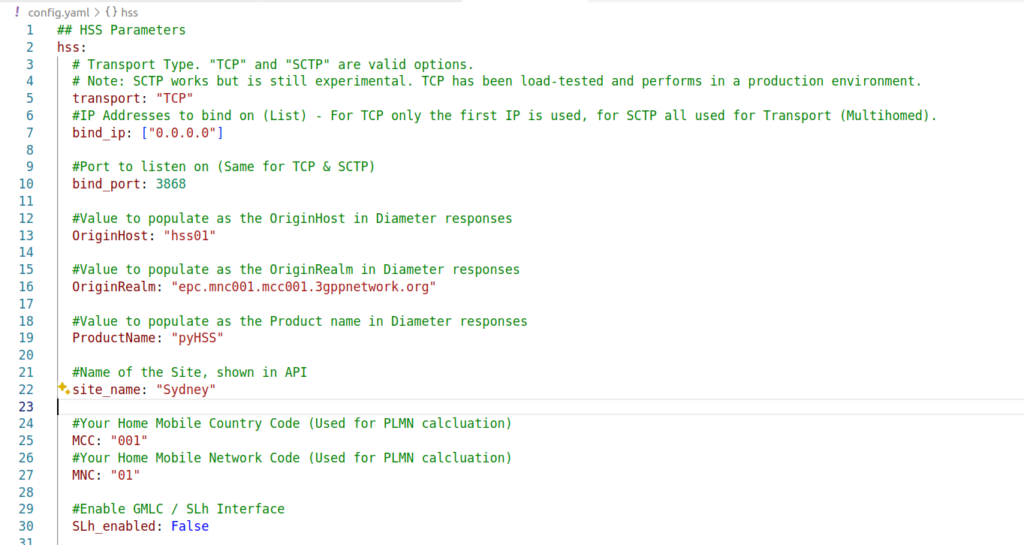
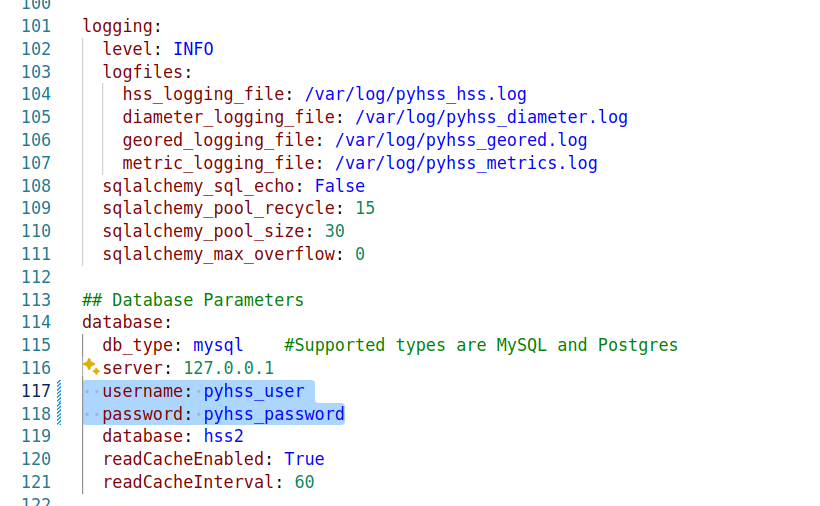
Lastly we’ll need to set the database parameters, updating the database: section to populate your credentials, setting your username and password and the database to match your SQL installation we setup at the start.
With that done, we can start PyHSS, which we do using systemctl.
Because there’s multiple microservices that make up PyHSS, there’s multiple systemctl files use to run PyHSS as a service, they’re all in the /systemd folder.
We’ll copy them all to our systemd folder.
cp /etc/pyhss/systemd/ /lib/systemd/system/
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start pyhss
And with that we’ve got PyHSS running and ready for a Diameter peer to connect.
Now you should be able to bring our Diameter peers up.
If you’re using something like Kamailio, with C-Diameter Peer, you can read about the config for that here, or FreeDiameter you can read about here.
In the next post, we’ll cover subscriber provisioning via the API.

I am having this error what could it be?
Started pyhss_geored.service – PyHSS Geored Service.
2025-01-14T16:54:54.391014+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: Traceback (most recent call last):
2025-01-14T16:54:54.411954+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: File “/etc/pyhss/venv/pyhss/services/georedService.py”, line 447, in
2025-01-14T16:54:54.423775+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: georedService = GeoredService()
2025-01-14T16:54:54.424255+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
2025-01-14T16:54:54.429985+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: File “/etc/pyhss/venv/pyhss/services/georedService.py”, line 42, in __init__
2025-01-14T16:54:54.430755+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: self.logger.error(“[Geored] Fatal Error – geored not enabled under geored.enabled, exiting.”)
2025-01-14T16:54:54.433705+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: ^^^^^^^^^^^
2025-01-14T16:54:54.436807+00:00 fernando python3[18482]: AttributeError: ‘GeoredService’ object has no attribute ‘logger’
2025-01-14T16:54:54.678062+00:00 fernando systemd[1]: pyhss_geored.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
2025-01-14T16:54:54.708044+00:00 fernando systemd[1]: pyhss_geored.service: Failed with result ‘exit-code’.
2025-01-14T16:54:54.713519+00:00 fernando systemd[1]: pyhss_geored.service: Consumed 2.075s CPU time.
I am having this problem: from messaging import RedisMessaging
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘messaging’
Where could I get this module. I am using a virtual environment in python and I can’t get the messaging module that has redisMessagin
Hi Nick,
If I run the steps you have mentioned to run the pyhss with the systemctl via systemd services, I am getting it like this. How to resolve this issue..? I am using the latest main version.
● pyhss_diameter.service loaded failed failed PyHSS Diameter Service
● pyhss_geored.service loaded failed failed PyHSS Geored Service
● pyhss_hss.service loaded failed failed PyHSS HSS Service
● pyhss_log.service loaded failed failed PyHSS Log Service
● pyhss_metric.service loaded failed failed PyHSS Metric Service
Any update here please..? Not able to find any information on this error:
from messaging import RedisMessaging
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘messaging’
Yesterday I figured out that this error can be overcome if we run the systemctl command for starting pyhss after loggin in as su user. (remember to install the requirements also after this su login)