Note: I’m lazily posting this as its been in my drafts folder for an exceedingly long time – Before going too much further, it’s worth pointing out that eMBMS never really made it anywhere – no production networks of note use eMBMS. I started researching it and my interest petered out once I discovered I couldn’t get any UEs or hardware that supported eMBMS.
Mobile networks are designed as point to point, all traffic is unicast.
But multicast and broadcast traffic is real, and becoming more common in some applications.
In areas where users stream the same radio program, or TV show, live, each of them is consuming the same data stream, but each one gets sent a unique copy of the data, on a resource block allocated to them for reception of the data.
If we have 10 users on a cell, each streaming a 5Mbps live video, that’s 50Mbps of capacity taken up on the radio / air interface.
If that stream was moved onto a eMBMS service, only 5Mbps of capacity would be used, regardless of how many people on the cell are consuming it.
For Mission Critical Push to Talk applications, the lack of broadcast/multicast support was highlighted again. For a PTT app with 10 users in a talk group, you’d need to schedule resource blocks for 10 users, and allocate 10 radio resources 10 times, send GTP packets 10 times, all to send the same data to 10 people.
So enter eMBMS – The Evolved Multimedia Broadcast and Multicast Service, providing multicast service for LTE.
Overall Architecture
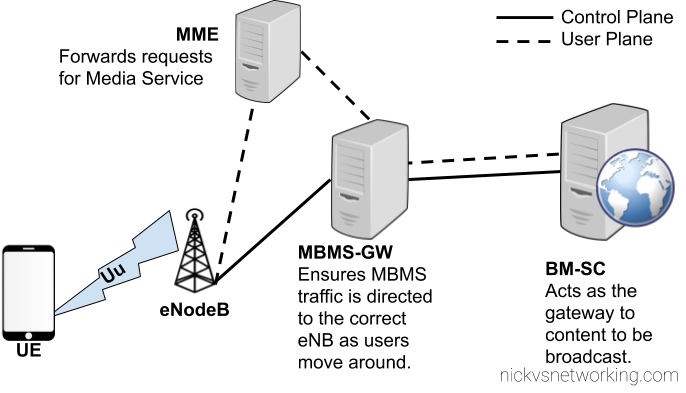
eMBMS introduces a few changes to the RAN side to handle support for a shared data channel, which is sent by the eNodeB and that UEs can listen on to get data. (More on admission control later)
From a core perspective two new network elements are introduced, the Broadcast/Multicast Service Center (BM-SC) and Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services Gateway (MBMS GW), these elements function in much the same was the P-GW and S-GW retrospectively, but in regards to Multicast services.
Like so many 3GPP specs before it, MBMS relies on GTP for transporting the data to be distributed, and relies on GTPv2-C for control plane data.
BM-SC – Broadcast Media Service Centre
The Broadcast Multicast Service Centre acts as the gateway between content providers (providing streams of data to be distributed) and the EPC.
The BM-SC sets up eMBMS sessions and pulls broadcast data from the content providers and collects receipts from subscribers of some streams to charge / track consumption of the services.
In this regard the BM-SC is akin to the P-GW, which as the border for the EPC and external networks, except it’s largely unidirectional.
MBMS Gateway
The MBMS Gateway (MBMS-GW) encapsulates the broadcast data stream from the BM-SC and encapsulates it into GTP packets to be distributed to eNBs across the network.
The MBMS-GW allocates a multicast transport address for each broadcast data stream?
MME Interaction
For this a new interface is introduced on the MME – the Sm interface, which interconnects the MME and the MBMS-Gateways assigned to it.
Key Interfaces / Reference Points
Sm Interface (MME <-> MBMS GW)
- MBMS Session Start Request/Response
- MBMS Session Update Request/Response
- MBMS Session Stop Request/Response
SGmb Interface (MBMS GW <-> BM-SC)
Control plane signaling
SGimb Interface (MBMS GW <-> BM-SC)
User Plane Signalling (Media)